AI
Semperoper Dresden to Open 2022-23 Season with AI-Composed Opera
The 3 things an AI must demonstrate to be considered sentient
9 AI-Generated Artworks Create the ‘Mona Lisa’ That Is Only Revealed When Put Together
Digital artist TDRAW used an AI art generator app to create a post-apocalyptic work of art made up of nine canvases.
Digital artist TDRAW specializes in artificial intelligence-generated art that explores fantastical worlds. One of his recently completed pieces depicts a cityscape from science fiction in nine different parts which, when put together, reveals another work of art: a silhouette resembling the portrait of the Mona Lisa.
Cheetah research results in new biomedical devices to support patient rehabilitation
How many times do we hear stories about how an ingenious solution to solve one challenge ends up being a perfect solution for something the inventor had never thought about? This is how South African researcher Amir Patel’s fascination with the speed and maneuverability of the cheetah led him to the health care arena. In devising methods to understand the way cheetah’s move, he has come up with a more affordable and accessible mechanism to support the rehabilitation of patients suffering injury or neurological disease.
Is it ethical to use AI-generated content without crediting the machine?
Artist Hides AI Faces Within Densely Patterned Paintings
Impact of AI on infringement and the enforcement of copyright and designs
How does AI play a part in the enforcement of IP rights, today.
On 2 March 2022, the “Study on The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on The Infringement and Enforcement of Copyright and Designs” was published by the Observatory. The purpose of this study is to analyse the impact of AI technologies on both the infringement and enforcement of copyright and designs.
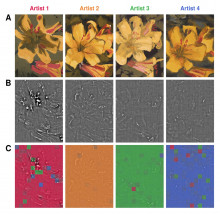
Researchers train AI to attribute paintings based on detailed brushstroke analysis
Art historians may have a new tool for settling the attribution of disputed paintings using artificial intelligence (AI) thanks to research by a cross-disciplinary team led by physicists at Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio. The research, published in November in the journal Heritage Science, shows how machine learning analysis of small sections of topographical scans of paintings—some as tiny as half a millimeter—was able to attribute the works to the correct artist with up to 96% accuracy.
Face to face with Ai-Da the robot artist
Self-portraits by ultra-realistic android go on show at Design Museum in London
She, if it can be called a she, began her career with abstract art but has now moved to self, if they can be called self, portraits and they are alarmingly good.
“She is getting better all of the time,” said Aidan Meller, the force behind Ai-Da, the world’s first ultra-realistic robot artist, who is the subject of a display at the Design Museum in London.